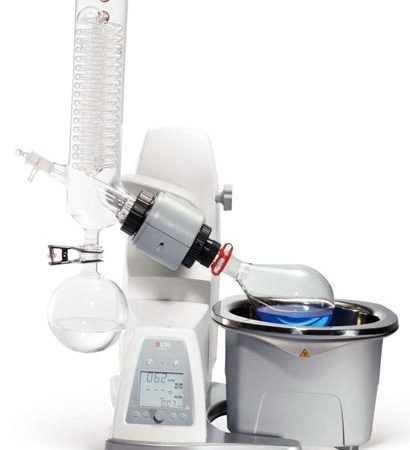
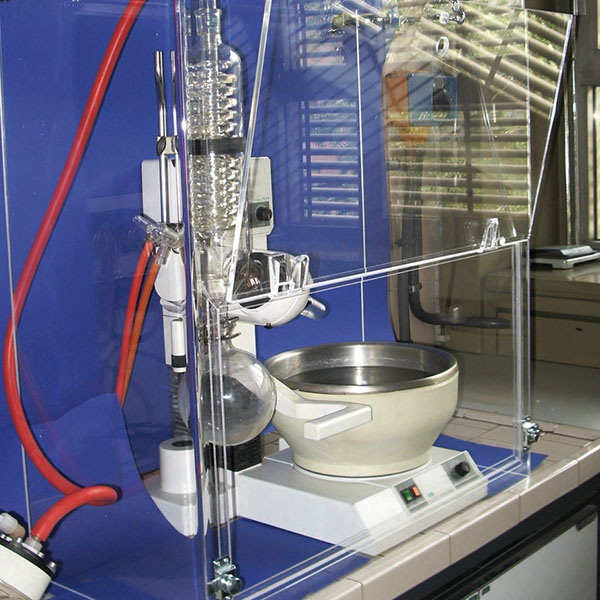
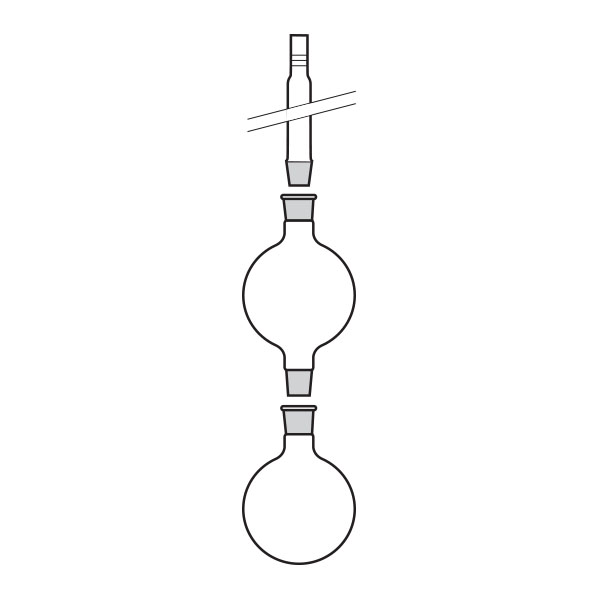
Evaporators are commonly called rotary evaporators. They are equipment designed to separate substances within a solution.
They are usually used to isolate solvents by vacuum evaporation.
Rotary Evaporator Components
The various components of rotary evaporators consist of:
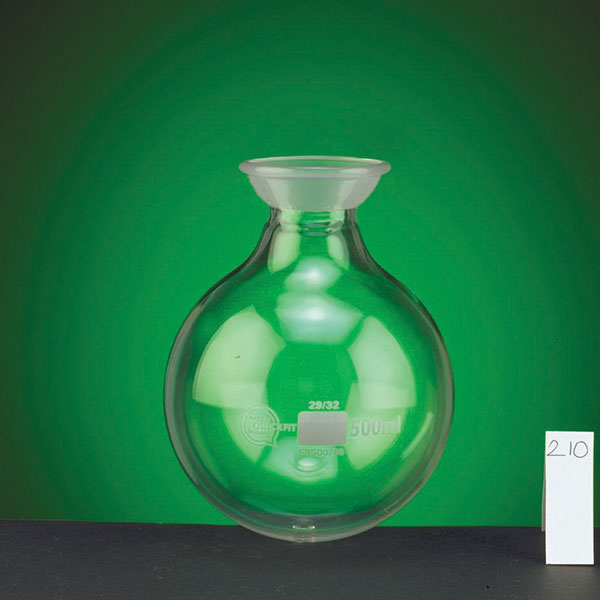
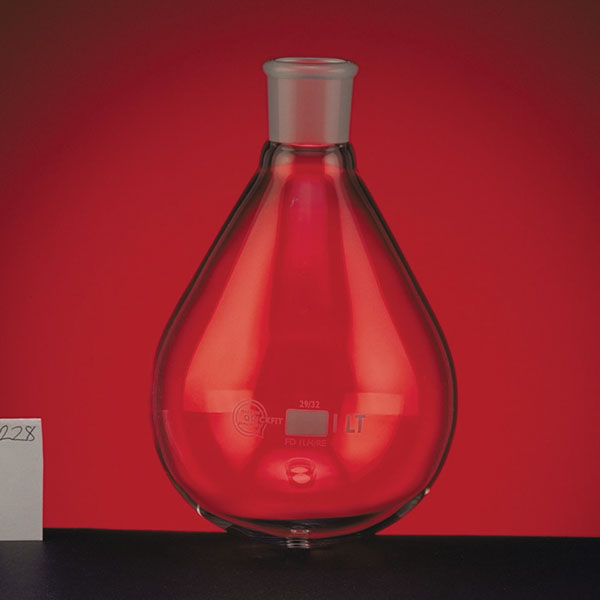
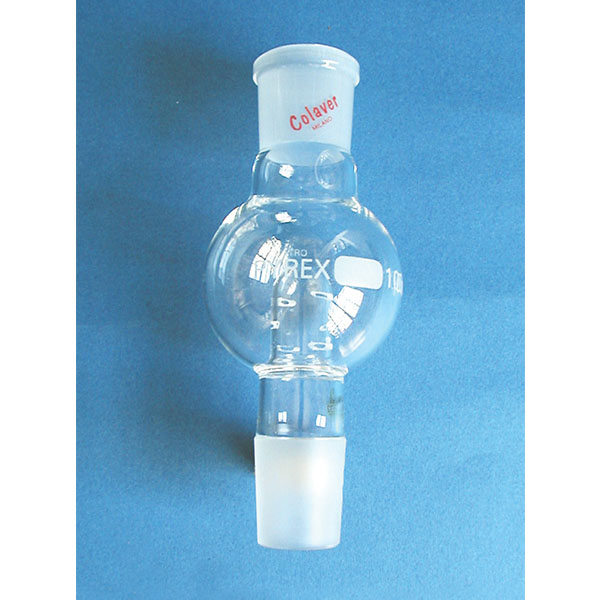
- an evaporation flask containing the solution to be evaporated;
.
- a thermostatic bath in which the evaporation flask is immersed to maintain the solution at the desired temperature;
- a motor whose purpose is to rotate the evaporation flask;
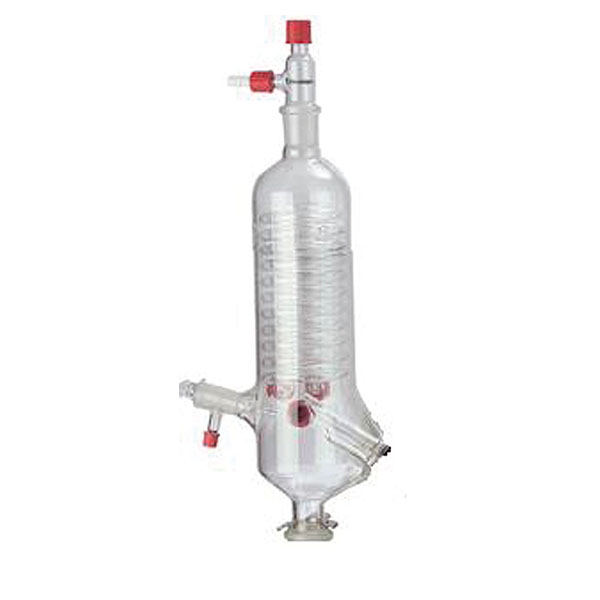
- an inclined or vertical cooler that serves to break down most of the vapours that develop with heating;
- a flask used to collect the solvents produced by condensation;
.
The condenser and flasks are made of glass. Sometimes plasticised glassware is used to ensure explosion-proof safety standards.
The whole system must be sealed to maintain the vacuum so the fittings must be tight.
Application of rotary evaporators
Rotary evaporators find their use mainly in organic synthesis laboratories.
Most common applications include those where the need is to rapidly concentrate solutions. They are particularly suitable when it is necessary to recover the solvent and the solute simultaneously and separately.
Dimensions and capacities
The most common laboratory rotary evaporators are those using evaporation flasks from 50 ml to 3,000 ml. The most common size flask is 1,000 ml.
But there are industrial applications that use large evaporators, with flasks from 10 to 50 litres.
The most popular brands
The most popular rotary evaporators in laboratories are mainly of two brands: Buchi and Heidolph. Both companies are distinguished by the high quality of their products and the precision of the instrumentation they apply.
But all glass parts can be purchased separately from any manufacturer.
In Colaver's blower shop it is possible to make coolers or other accessories with specific requirements for use with rotary evaporators.